Last quarter, a retail analytics team launched their competitive pricing strategy based on extraction from competitor websites. Within weeks, they'd slashed prices across 200 products. The result? A $340,000 revenue loss before anyone discovered the truth: their extraction tool had collected outdated promotional prices instead of current listings. The information was technically accurate when collected, but completely wrong for decision-making.
This scenario plays out daily across businesses worldwide. Collection technology has advanced tremendously by 2026, with AI-powered automation and no-code solutions making extraction accessible to everyone. But accessibility doesn't guarantee quality.
The real challenge isn't gathering information, it's ensuring what you collect is accurate, reliable, and actionable. We've seen companies make million-dollar mistakes because they trusted unvalidated extraction results. Quality assurance isn't optional; it's the foundation of successful intelligence gathering.

Throughout this guide, we'll walk you through our proven seven-step process for validation. You'll learn integrated quality control techniques that work whether you're extracting dozens of pages or operating at enterprise scale with millions of records. We'll cover AI-assisted validation methods, real-time monitoring systems, and specialized assessment tools that ensure your extraction projects deliver dependable results every time.
Key Takeaways
- Unvalidated extraction results can lead to costly business decisions and wasted resources that impact your bottom line
- Quality assurance must be integrated throughout your entire extraction workflow, not treated as a final checkpoint
- Our seven-step validation framework ensures accuracy at every stage from strategy design through automated monitoring
- AI-powered validation tools in 2026 enable real-time quality checks that catch errors before they affect decisions
- Specialized assessment techniques vary by information type, pricing requires different validation than contact details or product specifications
- Enterprise-scale projects with millions of records demand automated quality control systems, not manual reviews
Why Data Verification Is Critical for Web Scraping Success
Many companies spend thousands on web scraping only to find their data is useless. The real challenge lies in verifying the data. Without verification, even the most advanced scraping tools yield unreliable results, harming your business.
Today, businesses rely on precise data for decision-making, market analysis, and innovation. Poor web data quality disrupts every process. Your competitive analysis, automation, and market research suffer, leading you astray.
Understanding the importance of verification helps avoid costly errors. Let's examine the effects of unverified scraped data and why validation is essential in 2026.
The Real Cost of Unverified Scraped Data
Poor web data quality costs more than the initial scraping investment. Companies have lost over $50,000 in marketing spend on invalid email addresses. These losses are just the tip of the iceberg.
Consider a pricing team making decisions based on unverified competitor data. Errors in this data can price your company out of the market or leave revenue untapped. One e-commerce client corrected their pricing strategy, recovering nearly $200,000 in lost margin in just three months.
Teams must re-scrape data due to quality issues, wasting time and resources. Developers spend days fixing problems that verification would have caught immediately. Analysts waste time cleaning datasets instead of providing insights.
Failed automation initiatives also incur hidden costs. Bad data leads to bad outcomes. CRM systems with incorrect contact information fail to communicate. Inventory management systems with wrong product data cause stockouts or overstock.

Common Data Quality Issues That Undermine Your Projects
We often see the same problems in web scraping projects. Incomplete records are a major issue, missing critical fields like email addresses or pricing information. These gaps make datasets unusable.
Formatting inconsistencies break downstream systems that expect standardized input. Phone numbers, addresses, and dates come in various formats, requiring extra handling. Each variation complicates the verification process.
Duplicate entries inflate dataset size and distort analysis results. The same record appearing multiple times makes metrics unreliable. Your visitor counts, market size estimates, and trend analysis are all affected.
Here are the most frequent data accuracy in web scraping problems we identify:
- Structural errors: Data extracted from wrong page elements or misaligned fields
- Outdated information: Content that no longer reflects current reality
- Encoding issues: Special characters that display incorrectly
- Type mismatches: Numbers stored as text or dates in wrong formats
- Null value proliferation: Empty fields that should contain data
Each issue cascades through your data pipeline, amplifying errors at every stage. A single formatting inconsistency in the scraping phase becomes a system-wide failure when that data feeds into your automation platform. The earlier you catch these problems, the less damage they cause.
What Stakes Are Involved in 2026
The importance of data verification has grown significantly in recent years. Regulatory scrutiny around data accuracy has increased across multiple jurisdictions. Companies face penalties for making decisions based on unverified information, with severe consequences in regulated industries like finance and healthcare.
Modern business intelligence systems amplify the impact of bad data. When your analytics platforms process millions of records, even small error rates produce massive distortions. A 2% data quality problem in your source data becomes a 20% accuracy problem in your final reports.
Competitive disadvantage represents the highest stake. Your competitors who implement rigorous data scraping verification steps gain market insights you miss. They identify opportunities faster, respond to threats more quickly, and make better strategic decisions.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning systems raise the stakes even higher. These technologies consume vast amounts of data to train their models. Feed them unverified scraped data, and they learn incorrect patterns. Your AI-powered pricing engine makes bad recommendations. Your predictive analytics generate false forecasts.
The principle of garbage in, garbage out has never been more relevant. In 2026, with automation driving more business processes, you cannot afford to build on unreliable foundations. Every decision, every automation, every insight depends on data accuracy in web scraping.
Web data quality standards have evolved from nice-to-have features into business-critical requirements. Companies that skip verification steps discover their mistakes when it's too late, after bad data has already damaged customer relationships, distorted strategic planning, or caused compliance violations.
We've helped organizations implement proper verification frameworks after they've experienced these costly failures. The pattern is always the same: the investment in verification is a fraction of the cost of cleaning up the damage from unverified data. Smart teams build verification into their workflow from day one, treating it as an essential component, not an optional extra.
Understanding the Web Data Quality Landscape
Web data quality varies widely. Web scraping mimics human browsing but is faster and more precise. It involves sending requests to URLs, parsing HTML responses, and extracting specific data.
Several factors can affect data reliability. Understanding these challenges is key to effective verification strategies.
What Makes Scraped Data Unreliable
Several factors threaten web data quality. Website structure changes are a major issue. When a site's HTML layout changes, traditional scrapers often fail.
Dynamic content loaded via JavaScript is another challenge. Standard HTTP requests may miss data loaded after scripts execute. This can lead to missing critical information.
Anti-bot protections can also distort data. These systems detect automated access and may block requests or serve corrupted data. Their goal is to thwart scraping efforts.
Additional reliability issues include:
- Inconsistent data formatting across different pages or sections of the same website
- Temporal variations where content changes between scraping sessions
- Encoding problems that distort special characters and international text
- Incomplete page loads that result in partial data extraction
Adaptive approaches using AI can handle structural variations better. These systems learn patterns, improving data accuracy in web scraping.

Key Verification Metrics We Track
To validate scraped data effectively, we focus on five key quality dimensions. Each metric offers insights into different aspects of your dataset's reliability.
Completeness measures the percentage of required fields with actual values. For example, if you're extracting product listings with ten attributes, completeness shows how many records have all ten fields populated.
Accuracy confirms the correctness of extracted values. We spot-check random samples against the original web pages. Aiming for 95% or higher accuracy is common for critical projects.
Consistency ensures uniform formatting and structure across your dataset. Phone numbers should have the same format, dates should follow consistent patterns, and categorical values should match predefined standards.
We also track these critical metrics:
- Timeliness: Freshness and currency of the extracted information
- Validity: Conformance to expected data types and formats
- Uniqueness: Absence of duplicate records in your dataset
- Integrity: Proper relationships between connected data points
Setting acceptable thresholds depends on your project's needs. Financial data requires near-perfect accuracy, while less sensitive applications might tolerate higher error rates. It's wise to document these standards before scraping.
The Difference Between Validation and Verification
Validation and verification are often confused but represent distinct quality control processes. Understanding this distinction is vital for building robust verification systems.
Validation confirms data conforms to expected schemas and formats. This is about structural correctness. When validating scraped data, you're checking if an email field contains a properly formatted email address, if a price field contains a numeric value, and if required fields aren't empty.
Validation occurs during or immediately after extraction. It catches technical errors like parsing failures, type mismatches, and structural problems. These checks run automatically and provide instant feedback.
Verification confirms data is factually accurate and represents real-world truth. This is about semantic correctness. An email address might be perfectly formatted but fake. A phone number might pass format checks but be disconnected.
Verification often requires external checks against authoritative sources. For email addresses, this means connecting to mail servers. For phone numbers, it involves carrier lookups. For addresses, it requires postal service databases.
Both processes are essential and complementary. Validation catches technical errors during extraction. Verification ensures the extracted data is correct and usable for its intended purpose. We implement validation as the first line of defense and verification as the final quality gate before data enters production systems.
Step 1: Design Your Data Verification Strategy Before Scraping
A well-designed verification strategy transforms raw scraped data into a trustworthy business asset. Rushing into scraping without a clear plan for quality control often leads to project failures. The most successful data scraping verification process begins before you write your first line of code.
Planning ahead saves time, money, and frustration. Establishing verification standards upfront prevents data quality issues that would require expensive fixes later. This strategic approach ensures that every data scraping verification step aligns with your business objectives.
Establish Clear Quality Standards for Your Project
The first question we ask is simple: what does "good data" mean for your specific project? Without clear quality requirements, verifying scraped data or measuring success is impossible. We need to define concrete, measurable standards that everyone on the team understands.
Start by identifying which data fields are absolutely essential versus nice-to-have. Financial data typically requires 99% accuracy, while descriptive text fields might be acceptable at 95%. This distinction matters because it determines where we focus our verification efforts.
Next, we establish acceptable value ranges and formats for each field. Email addresses must match standard patterns. Phone numbers need specific digit counts. Dates require consistent formatting. These standards become the benchmarks we use throughout the data scraping verification process.
Data freshness requirements deserve special attention. Some projects need real-time data, while others can work with weekly updates. We document these timeframes clearly because they impact both scraping frequency and verification methods.

Create Verification Checkpoints Throughout Your Pipeline
We don't treat verification as a single end-of-process task. Instead, we build multiple checkpoints throughout the entire workflow. This layered approach catches errors early when they're easier and cheaper to fix.
Our verification workflow includes four critical stages. Pre-scraping checks validate that target URLs are accessible and return expected status codes. This prevents wasted resources on broken or blocked sources.
During-scraping validation happens in real-time as data flows through your scraper. We implement schema checks to ensure incoming data matches expected structures. Format validation catches issues like malformed emails or invalid phone numbers immediately.
The third checkpoint occurs post-extraction. This is where we apply specialized verification for specific data types. Email verification services check deliverability. Phone validation confirms number formats and carrier information. Address verification standardizes location data.
Lastly, we perform a complete dataset review before considering the project finished. This includes cross-validation against multiple sources, statistical anomaly detection, and logical consistency checks. When you understand how to verify scraped web data at each stage, you build confidence in your final dataset.
Choose the Right Verification Methods and Tools
The tools you select determine how effectively you can verify scraped data throughout your project. We balance automation with human oversight, choosing solutions that match our specific needs and budget constraints.
Built-in scraper validation features provide the first line of defense. Modern scraping frameworks include basic checks for response codes, timeouts, and data structure validation. These features catch obvious problems without additional infrastructure.
For specialized data types, we rely on third-party verification APIs. Email verification services check syntax, domain validity, and mailbox existence. Phone validation tools verify number formats, identify carriers, and flag disconnected lines. Address verification APIs standardize formatting and confirm deliverability.
Custom validation scripts fill the gaps where off-the-shelf solutions fall short. We write Python scripts for industry-specific validation rules, business logic checks, and proprietary data format requirements. These scripts integrate seamlessly into our data scraping verification steps.
Manual spot-checking remains valuable despite automation advances. We establish protocols for human reviewers to sample random records, verify edge cases, and identify patterns that automated systems might miss. This combination of automated and manual verification creates robust quality control.
The investment in premium verification services depends on your data volume and accuracy requirements. High-stakes projects with millions of records justify subscription services. Smaller projects might succeed with open-source tools and manual verification. We help you find the right balance for your situation.
Documentation ties everything together. We create clear procedures for each verification method, establish escalation paths for errors, and define quality thresholds that trigger alerts. This systematic approach ensures consistent results regardless of who runs the scraper.
Step 2: Set Up Your Scraping Infrastructure for Data Accuracy
Before extracting data, you must build a solid infrastructure for accuracy. The foundation you create determines the quality of your data. We've seen that early infrastructure choices greatly impact data quality throughout the scraping process.
Many teams start scraping without considering the impact of their tool choices on data accuracy. This approach leads to errors and compromised data quality. A well-configured infrastructure minimizes these risks and ensures reliable data collection.
Choose the Right Tools: Python, Selenium, and Playwright
Most scraping guides recommend browser automation tools, but they're not always necessary. We use python with the requests library for about 80% of our projects. It efficiently handles static HTML with minimal overhead. A requests call takes around 200 milliseconds, while browser-based methods take several seconds.
The requests library, paired with BeautifulSoup, offers the fastest and most cost-effective solution for static content. This combination allows for quicker data extraction, reduced server resource usage, and simpler code maintenance.
For dynamic content, you need browser automation tools. Selenium and playwright are essential for handling AJAX requests, infinite scrolling, and content that appears after user interaction.
Selenium has been the standard for years, providing extensive browser support and a mature ecosystem. We use it for complex interactions requiring precise browser control. But playwright has become our preferred choice in 2026 for handling JavaScript-rendered content.
Playwright offers several advantages that directly impact data accuracy:
- Faster execution speeds that reduce timeout errors and incomplete data collection
- More reliable element selectors that decrease failed extraction attempts
- Built-in waiting mechanisms that ensure content loads completely before extraction
- Better handling of modern web frameworks like React and Next.js
- Native support for multiple browser contexts without resource overhead
The decision logic is straightforward. Start with requests for static HTML. Use playwright when JavaScript rendering is required. Reserve selenium for legacy projects or specific browser behaviors not supported by playwright.
Configure Proxies for Clean Data Collection
Proxies are critical for obtaining accurate, unbiased data. Without proper proxy configuration, websites may serve different content, block requests, or provide skewed data.
We configure proxies to ensure data reflects real user experiences. This isn't about hiding, it's about accuracy. Geographic targeting requires proxies from specific locations to verify regional data accuracy.
HTTP Proxies vs SOCKS5 vs SOCKS4
Understanding proxy protocols is key to choosing the right solution for accuracy. Each protocol operates differently and serves specific use cases that affect data collection quality.
HTTP proxy servers work at the application layer, handling only HTTP and HTTPS traffic. They're the fastest option for web scraping, with the lowest latency and highest throughput. We use http proxies for standard scraping tasks where speed matters and detection systems are not sophisticated.
SOCKS4 proxy is the older, simpler protocol without authentication support. It offers basic functionality for TCP connections but lacks the security features of SOCKS5. We rarely use socks4 proxy options in 2026 unless working with legacy systems that don't support newer protocols.
SOCKS5 proxy servers operate at a lower network level, providing greater flexibility and anonymity. They support authentication, handle UDP traffic, and work with any protocol. SOCKS5 proxies offer better security and are harder for websites to detect as proxy traffic. We deploy socks5 proxy configurations when scraping sites with advanced anti-bot systems or when maintaining consistent sessions across multiple requests.
Here's a practical comparison to guide your selection:
- Speed priority: HTTP proxies deliver fastest performance for straightforward scraping
- Security needs: SOCKS5 proxies provide better anonymity and authentication options
- Protocol flexibility: SOCKS5 handles non-HTTP traffic when scraping requires additional protocols
- Legacy compatibility: SOCKS4 works with older systems but offers limited functionality
Elite Proxy Configuration Best Practices
Elite proxy servers provide the highest level of anonymity by not identifying themselves as proxies in request headers. Websites cannot detect that you're using a proxy, which is critical for collecting accurate data from sites with strict access controls.
We implement several best practices when configuring elite proxies for data accuracy:
- Rotation strategies: Rotate IP addresses on a schedule that mimics natural browsing patterns, not too fast to trigger rate limiting, not too slow to waste proxy resources
- Quality testing: Test each proxy before deployment by checking response times, success rates, and whether the proxy is properly anonymizing requests
- Geographic matching: Use proxies from the same geographic region as your target audience to ensure you're collecting regionally accurate data
- Authentication management: Implement secure authentication that doesn't expose credentials in your code or logs
- Performance monitoring: Track proxy health metrics during scraping runs to identify and replace underperforming proxies automatically
We also maintain a pool of backup proxies. When a proxy fails or gets blocked, our system automatically switches to an alternative without interrupting data collection. This redundancy ensures continuous operation and prevents data gaps that could compromise accuracy.
Set Up Headless Browsers and Antidetect Browsers
When scraping requires JavaScript execution, headless browser configurations allow you to render dynamic content while minimizing resource consumption. Headless browsers run without a visible interface, reducing memory usage and allowing you to operate multiple browser instances simultaneously for parallel scraping.
We configure headless Chrome and Firefox with specific flags that optimize performance without sacrificing data accuracy. Disabling unnecessary features like images and CSS when you only need text data can speed up scraping by 40-60%. But be cautious, some sites detect headless browsers and serve different content or block access entirely.
This is where antidetect browser technology becomes valuable. Antidetect browsers randomize browser fingerprints to make each session appear as a unique, legitimate user. They modify dozens of browser characteristics including:
- Canvas fingerprinting parameters that websites use for tracking
- WebGL rendering signatures that identify browser instances
- Font enumeration patterns that reveal system characteristics
- Screen resolution and color depth combinations
- Timezone and language settings that should match proxy locations
We implement antidetect browsers when scraping sophisticated sites that employ advanced detection systems. The additional complexity is justified when you're collecting high-value data from sources that actively block scrapers. By appearing as legitimate users, you ensure the data you collect accurately represents what real users experience.
Configuration matters significantly for data accuracy. We align antidetect browser settings with our proxy locations, if you're using a proxy from New York, your browser fingerprint should reflect a typical New York user's system configuration. Mismatches between proxy location and browser characteristics can trigger detection systems and result in blocked requests or manipulated data.
The infrastructure you establish in this step creates the technical foundation for everything that follows. With the right tools, properly configured proxies, and appropriately deployed browser automation, you're positioned to collect accurate data consistently across your scraping projects.
Step 3: Implement Real-Time Validation During the Scraping Process
The most effective verification happens while your scraper is actively collecting data. Waiting until after extraction completes means discovering problems too late, wasting server resources and time on corrupted datasets. Real-time validation gives us the power to catch errors immediately, adjust extraction logic on the fly, and ensure every record meets quality standards before it enters our database.
When we validate scraped data during extraction, we transform the entire scraping operation. Failed validations trigger immediate responses, allowing us to pause jobs, investigate selector issues, and prevent thousands of flawed records from accumulating. This proactive approach reduces post-processing time by up to 70% in our experience.
Modern scraping infrastructure in 2026 supports sophisticated validation frameworks that integrate directly into extraction workflows. These systems check data structure, format, completeness, and logic as each record is captured, creating a safety net that catches quality issues before they multiply.
Schema Validation Techniques
Schema validation establishes the structural blueprint that every scraped record must follow. We define schemas that specify required fields, optional fields, data types, nested object structures, and array constraints. This framework acts as a contract between our scraper and our data pipeline.
JSON Schema provides a powerful standard for defining validation rules. We create schema documents that describe expected data structures in detail, including field names, types, patterns, and constraints. When a scraped record doesn't match the schema, validation fails immediately with specific error messages identifying the mismatch.
Pydantic models in Python offer even more sophisticated web scraping data verification capabilities. We define data models as Python classes with type annotations, and Pydantic automatically validates incoming data against these specifications. The library handles type coercion, custom validators, and complex nested structures with minimal code.
- Required fields: product_name, price, availability status
- Optional fields: description, ratings, review_count
- Type constraints: price as float, ratings between 0-5, review_count as integer
- Format validation: URLs must include protocol, dates in ISO format
AI-powered scrapers in 2026 work seamlessly with schema validation. Modern AI tools like Grok understand semantic requirements and can structure extracted data to match predefined schemas automatically. The AI interprets page content contextually, making extraction more resilient to website changes.
We configure validation to run synchronously during extraction. Each scraped item passes through the schema validator before being queued for storage. Invalid items get flagged, logged with detailed error information, and optionally trigger retry logic with alternative extraction strategies.

Format Checking and Data Type Verification
Beyond structural validation, we need to verify that individual field values conform to expected formats. Different data types require specific validation approaches to ensure data accuracy in web scraping operations. Format checking catches subtle errors that schema validation might miss.
Email addresses require validation against RFC 5322 standards. We use regex patterns that check for proper structure: local part, @ symbol, domain name, and valid TLD. Format validation alone doesn't confirm deliverability, which is why we combine format checking with email verification services covered in later sections.
Phone number validation presents unique challenges due to international format variations. We implement validators that:
- Check for appropriate digit counts based on country codes
- Validate area codes against known valid ranges
- Remove formatting characters for consistent storage
- Flag numbers that don't match expected patterns for manual review
URL validation ensures that scraped links are properly formatted and functional. We verify protocol presence (http/https), check domain syntax, validate path structures, and optionally perform HEAD requests to confirm URLs are accessible. This prevents broken links from polluting our datasets.
Date and timestamp validation requires parsing strings into standardized formats. We handle various input formats (MM/DD/YYYY, ISO 8601, Unix timestamps) and convert them to consistent representations. Range checks ensure dates fall within reasonable boundaries, catching obvious errors like future publication dates on historical content.
Numeric values need type verification and range validation. Prices should be positive floats within market-reasonable ranges. Quantities should be positive integers. Ratings typically fall between defined min/max values. We create reusable validation functions for each numeric type that check both format and logical constraints.
Completeness and Null Value Checks
Missing data represents one of the most common quality issues in web scraping. We need systematic approaches to identify incomplete records and distinguish between legitimate empty fields and extraction failures. Completeness checks protect against silently broken scrapers that appear to run successfully but capture no useful data.
We establish acceptable thresholds for missing data based on field importance. Critical fields like product names or prices should have near-zero null rates. Secondary fields like extended descriptions might allow 20-30% missing values. When null rates exceed thresholds, our system flags possible scraper malfunctions.
Field-level completeness tracking reveals patterns in extraction failures. If a specific field consistently comes back empty across multiple records, the selector has likely broken due to website changes. We monitor these metrics in real-time to validate scraped data quality as extraction proceeds.
Distinguishing intentional empty fields from extraction errors requires context. A product legitimately might lack reviews (review_count = 0), but a missing product name always indicates an error. We encode this domain knowledge into our validation rules, treating different null values appropriately based on field semantics.
Fallback extraction strategies activate when primary selectors fail. We define secondary and tertiary extraction paths for critical fields. If the primary CSS selector returns null, the system automatically tries alternative selectors, XPath expressions, or regex patterns. This resilience improves completeness rates significantly.
Record-level completeness scores help us prioritize data quality. We calculate the percentage of non-null required fields for each record. Items below completeness thresholds get flagged for enhanced validation, manual review, or re-scraping. This scoring system allows us to make informed decisions about which records to keep or discard.
Immediate Error Flagging Systems
Real-time alerting transforms how to verify scraped web data from a post-mortem analysis into an active monitoring process. When validation failures occur during extraction, we need immediate notification to prevent wasting resources on failed scraping runs. Error flagging systems provide this critical feedback loop.
We implement tiered alert systems based on error severity and frequency. Single validation failures might log warnings without interrupting the scrape. Sustained failure rates above defined thresholds trigger immediate notifications via email, Slack, or SMS. Critical errors like authentication failures or IP blocks halt scraping jobs immediately.
Logging strategies capture both successes and failures with sufficient detail for debugging. Each validation check generates structured log entries including:
- Timestamp: when the validation occurred
- Record identifier: URL or unique ID of the scraped item
- Validation type: schema, format, completeness, or logic check
- Pass/fail status: clear indication of validation outcome
- Error details: specific description of what failed and why
Dashboard visualization gives us at-a-glance web scraping data verification status. We monitor success rates, error distributions, field-level completeness, and extraction speed in real-time. Anomaly detection algorithms identify sudden changes in validation metrics that might indicate scraper breakage.
Automatic pause mechanisms protect against runaway failures. When error rates exceed configured thresholds, the system pauses extraction, sends detailed error reports, and waits for manual intervention. This prevents accumulating thousands of invalid records that would require later cleanup.
Error categorization helps prioritize fixes. We classify validation failures into categories like selector errors, format mismatches, completeness issues, and logical inconsistencies. Understanding error distribution guides troubleshooting efforts and helps identify root causes quickly.
Integration with monitoring tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or Datadog provides enterprise-grade observability. We export validation metrics to these platforms for historical tracking, trend analysis, and correlation with infrastructure metrics. This ensures data quality remains high across all scraping operations.
By implementing these real-time validation practices, we catch quality issues at the source. This proactive approach to verification fundamentally changes how we manage scraping projects, reducing debugging time and ensuring consistent data quality from the first record to the last.
Step 4: How to Verify Scraped Web Data Using Specialized Verification Tools
The fourth step in our data verification process focuses on leveraging dedicated verification platforms. These platforms go beyond simple format checks to validate the real-world usability of your scraped contact data. While format validation confirms that data looks correct, specialized verification tools actually test whether email addresses can receive messages, phone numbers connect to active lines, and physical addresses represent deliverable locations. This distinction makes all the difference between data that appears clean and data that actually works in production environments.
Specialized verification services solve a critical problem we frequently encounter in web scraping projects. You can collect thousands of perfectly formatted email addresses, phone numbers, and mailing addresses, but without verification, a significant percentage will be invalid, disconnected, or undeliverable. This creates serious downstream problems: bounced emails damage sender reputation, disconnected phone numbers waste sales team time, and invalid addresses result in returned mail and wasted marketing spend.
We integrate verification tools at this stage because they require already-validated data formats to function effectively. These services expect standardized inputs and return detailed verification results that inform our next steps in the data quality pipeline.
Email Verification at Scale: Tools and Techniques
Email verification represents one of the most critical verification steps for scraped contact data. Format validation alone tells us nothing about whether an address actually exists or can receive messages. An email address might have perfect syntax but belong to a deleted account, a spam trap, or a domain that no longer accepts mail. Using unverified email addresses in marketing campaigns leads to bounce rates that can quickly damage your sender reputation and deliverability.
We implement email verification at scale by using services that perform multiple validation checks beyond simple format analysis. The verification process examines several critical factors that determine whether an email address is legitimate and active.
Professional email verification services check syntax to confirm RFC compliance, validate domain existence through DNS lookups, verify MX records to ensure the domain can receive email, and perform SMTP handshakes to confirm the specific mailbox exists without actually sending a message. Advanced verification also identifies disposable email addresses from temporary email services, detects role-based addresses like info@ or support@ that often have lower engagement, and flags known spam traps that can severely damage sender reputation.

Online Email Verification Services
Online email verification services have evolved significantly, providing sophisticated validation capabilities through simple API integrations. These platforms process verification requests in real-time or batch modes, depending on your workflow requirements and volume needs.
When we evaluate verification services, we focus on several key capabilities. Verification accuracy rates should exceed 95% for valid/invalid determinations. Processing speed matters for real-time integrations, with most quality services returning results in under two seconds per address. The service should provide detailed result codes, enabling nuanced decisions about data quality.
The best email verification tool options also include catch-all detection, which identifies domains configured to accept mail for any address, making individual mailbox verification impossible. They detect syntax issues that might pass basic regex validation, identify temporary email providers, and flag addresses with historical bounce patterns.
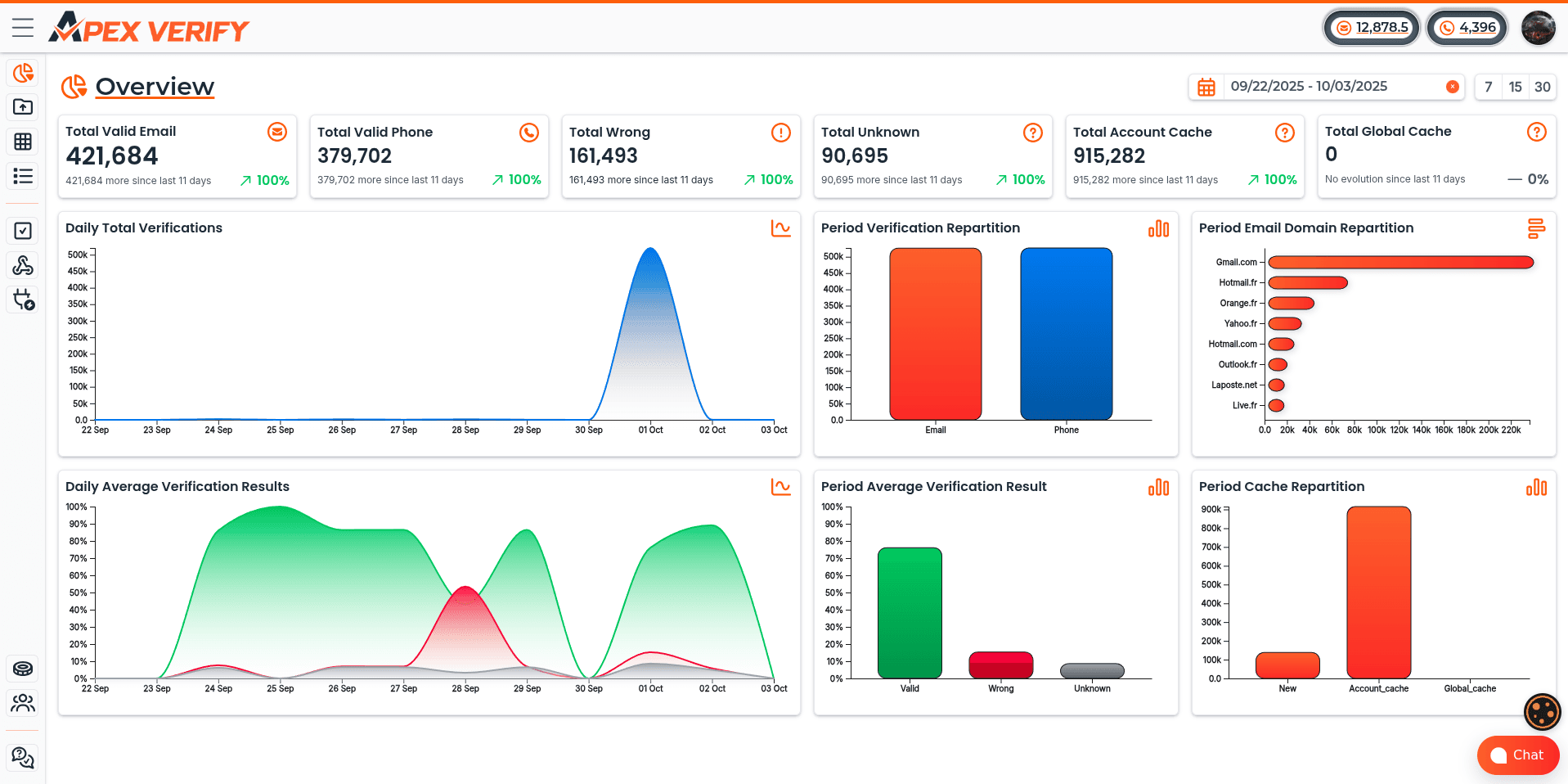
Implementing ApexVerify for Email Verification
We frequently implement ApexVerify as our email verification solution because it provides complete verification capabilities through a straightforward API integration. The platform handles both real-time verification during scraping and batch processing for large datasets, giving us flexibility to choose the approach that best fits each project's requirements.
ApexVerify performs multi-level verification checks that include syntax validation, domain verification, SMTP validation, and deliverability assessment. The service returns detailed results with confidence scores, enabling us to make informed decisions about borderline cases.
For real-time integration, we implement API calls immediately after scraping each email address. This approach provides instant feedback about data quality and allows us to flag problematic sources before collecting large volumes of bad data. For batch processing, we collect scraped emails into datasets and submit them for verification in bulk, which offers cost advantages and faster overall processing times for large projects.
The verification results include status codes like valid, invalid, catch-all, disposable, role-based, and unknown. Each result includes a confidence score from 0-100, helping us establish quality thresholds. We typically keep emails with confidence scores above 90, flag scores between 70-90 for manual review, and discard scores below 70 as unreliable.
Phone Number Verification at Scale
Phone number verification presents unique challenges because scraped phone numbers come in countless formats, may include extensions or additional text, and can represent mobile, landline, or VoIP services with different characteristics and value for business purposes. Simply confirming that a number has the right digit count tells us nothing about whether the number actually connects to an active line.
When we implement phone verification at scale, we focus on three primary objectives: confirming the number is active and can receive calls or texts, identifying the line type to understand how best to use the number, and standardizing formats for consistency across our dataset. These verification steps transform scraped phone numbers from uncertain data into reliable contact points.
Online Phone Number Verification Methods
Online phone number verification services use a combination of database lookups, carrier queries, and live connectivity tests to validate phone numbers without actually calling them. This verification happens through telecommunications databases that track number assignments, portability, and status.
The verification process starts with format standardization, converting various input formats into E.164 international format. This standardization ensures consistent formatting and enables accurate database lookups. The service then performs carrier lookup to identify the telecommunications provider and line type, determines whether the number is mobile, landline, or VoIP, and checks activation status to confirm the number is currently in service.
A quality phone number verification tool also provides geographic validation, confirming the area code and location match expected regions. It identifies prepaid versus postpaid lines, which can indicate data quality and user demographics. Some services offer risk scoring based on historical fraud patterns or spam complaints associated with the number.
ApexVerify handles phone verification through the same unified platform used for email verification. This integration simplifies workflows by providing a consistent API interface for multiple data types. The service validates phone numbers across international formats, identifies carrier and line type, confirms current activation status, and flags high-risk or fraudulent numbers based on pattern analysis.
Address Verification and Standardization
Physical address verification represents perhaps the most complex verification challenge because addresses involve multiple components, follow different formatting conventions across regions, and may be abbreviated or incomplete in source data. An address might look plausible but represent a location that doesn't exist, contains an invalid unit number, or cannot receive mail delivery.
We implement address verification to confirm that scraped addresses represent real, deliverable locations. This verification involves parsing address components, standardizing formats to postal service conventions, confirming the location exists through geocoding, and assessing deliverability for mailing purposes.
Online Address Verification Solutions
Online address verification services connect to postal databases and geocoding systems to validate addresses against authoritative sources. These platforms parse inconsistent address formats, correct common errors, and return standardized addresses with delivery point validation.
The verification process begins with address parsing, which breaks addresses into standardized components: street number, street name, unit designation, city, state, and postal code. This parsing handles various input formats and identifies components even when addresses are poorly formatted or contain extraneous information.
A thorough address verification tool performs standardization to convert addresses into formats that match postal service databases. For United States addresses, this means USPS standardization with approved abbreviations and formatting. The service validates each component against official records, confirms the postal code matches the city and state, and verifies that the street and number combination exists.
Geocoding provides additional validation by converting addresses to geographic coordinates. This confirms the location physically exists and enables distance calculations for logistics planning. Deliverability assessment checks whether the address can receive mail, flagging locations like PO boxes when physical addresses are required, identifying vacant properties, and detecting addresses flagged as undeliverable by postal services.
When implementing address verification at scale, batch processing offers significant efficiency advantages. We can verify thousands of addresses in minutes through bulk API submissions. The verification results indicate whether addresses are valid, invalid, or uncertain, and provide corrected, standardized versions of valid addresses.
All-in-One Data Verification with ApexVerify.com
Managing multiple verification services creates unnecessary complexity in data workflows. Each platform has its own API, billing system, dashboard, and data formats. We've found that consolidating verification through a single platform dramatically simplifies integration and reduces operational overhead.
All-in-one data verification platforms like apexverify.com provide unified solutions that handle email, phone, and address verification through consistent interfaces. This consolidation delivers multiple benefits that extend beyond mere convenience.
A unified platform offers a consistent API design across all verification types. Instead of learning and integrating three separate APIs, we implement a single integration pattern that handles multiple data types. This reduces development time and simplifies maintenance as our scraping projects evolve.
Volume discounts become more accessible when all verification runs through one provider. Instead of splitting verification volume across multiple services, we concentrate our usage to reach higher discount tiers more quickly. This can reduce verification costs by 30-50% compared to using separate providers for each data type.
The unified dashboard provides centralized monitoring of verification metrics across all data types. We can track verification volumes, accuracy trends, and cost allocation from a single interface. This visibility enables better quality monitoring and budget management compared to juggling multiple service dashboards.
When we implement ApexVerify for complete data verification, we gain additional advantages through integrated verification workflows. The platform enables sequential verification where email verification results can trigger phone verification for high-value contacts. We can establish unified quality scoring that combines verification results across data types. The service maintains consistent data handling and privacy practices across all verification types, simplifying compliance management.
Cost analysis consistently shows that consolidated verification reduces both direct verification costs through volume discounts and indirect costs through simplified integration and management. For projects requiring verification of multiple contact data types, a unified platform like apexverify.com delivers superior efficiency and cost-effectiveness compared to managing separate verification services.
Understanding how to verify scraped web data using specialized tools transforms the reliability of your datasets. These verification services validate that your data is not just formatted correctly but actually functional in real-world applications, protecting your projects from the costly consequences of working with unverified contact information.
Step 5: Navigate Anti-Bot Systems and Technical Challenges
Anti-bot systems pose a significant hurdle in collecting verified web data at scale. These systems detect automated scrapers, either blocking access or serving altered content. Modern anti-bot technologies use behavioral analysis and device fingerprinting to distinguish humans from bots.
We recommend starting with simple, respectful scraping techniques. Adding human-like behavior patterns, such as random delays and rotating user agents, helps avoid detection. For tougher sites, headless browsers with stealth configurations are necessary.
The principle guiding our approach is respectful data collection. Our goal is to gather data without overwhelming servers or bypassing security measures. This ensures sustainable scraping practices that maintain data quality and respect website resources.

Bypassing Captcha and Google reCAPTCHA
Captcha challenges appear when websites detect suspicious behavior patterns. Understanding why captcha systems trigger helps us avoid them more effectively. Most captcha implementations activate based on request frequency and behavioral anomalies.
We focus on prevention strategies first. Proper request pacing with random delays between 2-5 seconds mimics human browsing patterns. Complete browser fingerprints signal legitimate browser activity.
When Google reCAPTCHA appears, we have several options. Rotating residential proxies can reset reputation scores associated with IP addresses. Maintaining browser sessions with cookies and local storage demonstrates continuity.
For projects where captcha solving becomes unavoidable, third-party services provide API access to human solvers or machine learning solutions. We emphasize that relying on these services indicates our scraping approach needs refinement.
Ethical and legal considerations surround bypassing security measures. Many terms of service explicitly prohibit automated access. We always recommend reviewing legal requirements and considering whether APIs or data partnerships offer legitimate alternatives.
Dealing with Bot Detection Systems
Enterprise anti-bot platforms have become increasingly sophisticated. They use machine learning and behavioral analysis to identify automated traffic. Understanding how major platforms operate helps us configure scrapers that generate cleaner, more reliable data.
The three dominant enterprise bot detection systems, Cloudflare, Akamai, and Imperva, each employ distinct detection methodologies. We need tailored approaches for each platform to maintain data collection consistency and verification accuracy.
Understanding Cloudflare Challenges
Cloudflare's bot management works through multiple verification layers. JavaScript challenges verify browser execution capability. Browser integrity checks detect automation tools by examining browser APIs and inconsistencies in their implementation.
Rate limiting blocks excessive requests from single sources, while challenge pages require solving before accessing content. We've found that proper header configuration forms the foundation for working with Cloudflare-protected sites. Request pacing that stays well below rate limits prevents triggering more aggressive challenges.
Using headless browsers configured to pass JavaScript challenges proves essential. Tools like Playwright and Selenium with stealth plugins can execute Cloudflare's JavaScript without detection when properly configured. The key lies in disabling automation indicators that Cloudflare scans for.
Working Around Akamai Protection
Akamai's sophisticated bot detection employs behavioral analysis that identifies non-human interaction patterns. Their system examines timing consistency, mouse movements, scroll behavior, and keystroke dynamics. Device fingerprinting recognizes and blocks known automation tools by comparing browser characteristics against databases of bot signatures.
Adaptive challenges increase difficulty for suspected bots, creating a progressive barrier. We reduce detection likelihood through several approaches. Residential proxy rotation distributes requests across different IP addresses with clean reputations.
Randomizing interaction timings prevents the consistent patterns that Akamai's behavioral analysis flags. Session persistence maintains cookies and storage across requests, demonstrating continuity that reCAPTCHA algorithms recognize.
Imperva and Advanced Detection
Imperva represents enterprise-grade protection that includes machine learning-based detection, network-level blocking, and integrated DDoS protection. Their system analyzes traffic patterns at multiple layers simultaneously. This makes Imperva one of the most challenging platforms to work with.
When scraping Imperva-protected sites requires professional proxy services and residential IP rotation, we know we're dealing with serious protection. Network-level fingerprinting can identify data center IPs and block entire ranges. Only residential IPs with clean reputation scores typically succeed.
Browser automation must be nearly perfect, with complete fingerprints that match real devices exactly. Any inconsistency between claimed browser identity and actual capabilities triggers detection. For high-value data behind Imperva protection, we often recommend exploring legitimate API access or data partnerships.
Managing HTTP Headers and User-Agent Strings
Specific http headers must be configured to appear as legitimate browser traffic. Missing or misconfigured headers immediately flag requests as automated. We configure complete header sets that match real browsers precisely, as even minor deviations can trigger bot detection algorithms.
The user-agent string identifies the browser and operating system. We use current, popular combinations like Chrome on Windows or Safari on macOS. The Accept header specifies expected content types, typically including text/html, application/xhtml+xml, and other formats browsers request.
Additional critical headers include:
- Accept-Language: Indicates language preferences (e.g., "en-US,en;q=0.9")
- Accept-Encoding: Specifies compression support (e.g., "gzip, deflate, br")
- Connection: Controls connection persistence (typically "keep-alive")
- Referer: Shows the previous page when appropriate for navigation flow
- DNT: Do Not Track preference (increasingly common)
Here's an example of complete http headers for Chrome on Windows:
- User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/121.0.0.0 Safari/537.36
- Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8
- Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.9
- Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
- Connection: keep-alive
Rotating headers convincingly requires maintaining consistency within each session. We don't change the user-agent mid-session, as browsers never do this. Instead, we vary headers between sessions while keeping each session internally consistent. This approach mimics how different users with different browsers access the same site.
Browser Fingerprinting and Automation Detection
Sites identify automated browsers through fingerprint analysis that examines dozens of browser characteristics simultaneously. Canvas fingerprinting reads how browsers render graphics, creating unique signatures based on rendering engine differences. WebGL fingerprinting analyzes 3D graphics capabilities, while audio context fingerprinting examines audio processing characteristics.
Font enumeration reveals installed fonts, plugin detection identifies browser extensions, and WebDriver detection identifies Selenium and similar automation tools. The navigator.webdriver property returns true in automated browsers, immediately flagging them as bots.
We employ several configuration techniques to reduce fingerprint detectability. Disabling WebDriver flags removes the most obvious automation indicator. In Selenium, we use options like .add_experimental_option('excludeSwitches', ['enable-automation']) to hide automation signals.
Randomizing canvas output prevents consistent fingerprints across sessions. Stealth libraries for Puppeteer and Playwright automatically handle many fingerprint inconsistencies. These tools modify browser behavior to match human patterns more closely.
Antidetect browsers provide pre-configured fingerprint resistance, creating believable profiles that pass sophisticated detection systems. The key to successful bot detection navigation lies in gradual escalation. We start with basic configurations and only add complexity when simpler approaches fail. This strategy minimizes resource investment while maximizing data quality and verification accuracy throughout our scraping projects.
Step 6: Clean and Standardize Your Scraped Dataset
Once you've collected web data, the real work begins with transforming inconsistent raw information into a standardized format. Raw scraped data contains formatting irregularities, encoding issues, and structural problems that make it unsuitable for immediate use. We need to apply systematic cleaning and standardization processes to ensure our scraped data verification efforts deliver reliable results.
This transformation phase bridges the gap between extraction and analysis. Without proper cleaning, even perfectly extracted data can compromise your projects. The goal is to convert messy web data into consistent, verified scraped data that meets your quality standards and supports accurate business decisions.
Our Systematic Approach to Data Cleansing
Data cleansing for web scraping requires a methodical process that addresses common extraction artifacts. We start by removing HTML tags and entities that survived the initial extraction phase. These remnants can corrupt your dataset if left unaddressed.
Our cleansing pipeline handles several critical tasks systematically. First, we strip unwanted characters like special symbols and control characters that browsers render but databases reject. Second, we trim excessive whitespace while preserving meaningful spacing in product descriptions and addresses.
Text encoding standardization forms another key step. We convert all scraped content to UTF-8 format to handle international characters consistently. This prevents display issues and ensures compatibility across different systems and platforms.
We also correct obvious extraction errors during this phase. Merged fields where two data points ran together get separated. Truncated values that got cut off during extraction trigger re-scraping attempts or flagging for manual review.
Documentation plays a vital role in our cleansing process. We record every transformation rule applied to the dataset. This documentation allows team members to understand exactly how raw data became verified scraped data and enables consistent application across all records.
Normalization and Standardization Techniques
Different websites format the same information in countless ways. A price might appear as "$19.99", "19.99 USD", or "19,99 €". Our normalization techniques create uniformity from this chaos, making scraped data verification more reliable.
We apply specific transformations for each data type we encounter. Price values convert to a standard currency and numeric format without symbols. Date values transform to ISO 8601 format (YYYY-MM-DD), eliminating ambiguity between different regional formats.
Phone numbers present particular challenges across international datasets. We normalize them to E.164 international format, which provides a consistent structure regardless of source formatting. This standardization dramatically improves match rates when cross-referencing records.
Address normalization involves converting text to title case and applying standard postal abbreviations. "123 main street" becomes "123 Main St" following USPS guidelines. This consistency improves web data quality and enables better deduplication.
Categorical values require careful attention during standardization. Variations like "in stock," "available," and "in-stock" all represent the same status. We map these variations to single standard values, creating clean categorical data for analysis.
We preserve original raw values alongside normalized versions whenever possible. This practice maintains data lineage and allows reprocessing if normalization rules need adjustment. You can always refer back to the source data when questions arise.
Effective Deduplication Strategies
Duplicate records inflate dataset size and distort analysis results. Web scraping commonly produces duplicates when crawling multiple pages or revisiting URLs. Our deduplication strategies identify and eliminate these redundancies while preserving unique information.
Hash-based exact matching provides the fastest deduplication method. We generate unique hash values for each record based on key fields. Identical hashes indicate exact duplicates that we can safely remove without further analysis.
Fuzzy matching handles near-duplicates with minor variations. A product listed as "Samsung Galaxy S23" on one page and "Samsung Galaxy S23 Smartphone" on another represents the same item. We use similarity algorithms to identify these matches based on configurable thresholds.
Field-specific deduplication focuses on unique identifiers. When records contain SKUs, email addresses, or product IDs, we can define duplicates based solely on these fields. This approach works well when you know certain fields must be unique.
Deciding which duplicate to keep requires strategic thinking. We typically retain the most recent record, the most complete record, or create merged records combining information from all duplicates. The choice depends on your specific use case and data requirements.
Addressing Missing and Incomplete Data
No scraping project captures 100% of target data perfectly. Missing values and incomplete records require careful handling to maintain web data quality without unnecessarily discarding useful information.
We first determine whether missing data warrants re-scraping attempts. If a product price is missing, we usually initiate another extraction attempt. For less critical fields, we may accept the gap and flag the record appropriately.
Setting incompleteness thresholds helps manage partially complete records. We typically discard records missing more than 40% of required fields. These records provide too little value to justify keeping and processing through your pipeline.
Data imputation techniques fill certain types of missing values intelligently. We might use average values for numeric fields, most common values for categories, or predictive models based on related data points. But we apply imputation cautiously to avoid introducing inaccuracies.
Critical data that's too incomplete to use but too valuable to discard gets flagged for manual review. Human judgment often resolves edge cases more effectively than automated rules. This hybrid approach balances efficiency with accuracy in your scraped data verification workflow.
After completing these cleaning and standardization steps, your dataset should be consistent, deduplicated, and ready for the next verification phase. The effort invested here pays dividends in analysis accuracy and system compatibility downstream.
Step 7: Perform Cross-Validation and Accuracy Checks
We've reached the advanced verification stage, where multiple layers of accuracy checks transform questionable data into reliable business intelligence. After completing format and structure validation, deeper verification methods are needed. These methods confirm your information matches reality. This step goes beyond checking whether data looks right to confirming it is right.
Cross-validation techniques examine your scraped data from multiple angles. They catch errors that pass through earlier validation stages. These methods help you validate scraped data with confidence before using it in critical business decisions.
Cross-Reference Multiple Data Sources
The most powerful way to verify scraped data involves collecting the same information from multiple websites and comparing results. This technique identifies discrepancies and confirms accuracy through consensus. When three different sources agree on a data point, you can trust its correctness.
We implement cross-referencing workflows by scraping parallel data sources systematically. For product information, we extract data from manufacturer websites, retailer sites, and review platforms. Each source provides a different perspective on the same product.
Our cross-referencing process follows these steps:
- Scrape the same data points from three to five independent sources
- Establish consensus rules that accept values appearing in at least two out of three sources
- Flag discrepancies for manual review when sources disagree significantly
- Weight sources differently based on their historical reliability and authority
- Document which sources confirmed each data point for audit trails
Price comparison scenarios demonstrate this technique perfectly. When we check product prices across multiple retailers, we often discover pricing errors on individual sites. One retailer might display an outdated price while three others show the current market rate.
Contact information verification works in a similar way. We cross-check business details against multiple directories, social media profiles, and official websites. If a phone number appears consistently across four sources but differs on one, we know which version to trust.
This approach multiplies your scraping effort initially. But it dramatically increases confidence in data accuracy in web scraping, which is vital for high-stakes applications. The investment pays off when your decisions depend on correct information.
Implement Logical Consistency Validation
Logical consistency validation examines data relationships and business logic, not just format. These rules catch errors that look structurally correct but make no practical sense. We verify scraped data against real-world constraints and domain knowledge.
Range checks ensure values fall within sensible bounds. Product prices should exist between $0.01 and reasonable upper limits for their category. A consumer electronics item priced at $0.00 or $10,000,000 triggers immediate review.
Relationship validation confirms that related fields remain logically consistent. If an "in_stock" field shows false, then "quantity_available" should be zero. When "shipping_weight" is blank, "requires_shipping" cannot be true.
Temporal consistency checking verifies that dates follow logical sequences. A product's created_date must precede its modified_date. An order's shipped_date cannot occur before its ordered_date. These violations indicate data corruption or scraping errors.
Cross-field validation rules establish dependencies between data elements. Geographic data provides clear examples: if "country" equals "United States," then "state" must contain a valid US state abbreviation. If "zip_code" starts with "902," then "state" should be "CA" for California.
We implement these checks as automated validation functions that run immediately after extraction. Each validation rule returns pass/fail results with specific error messages. This systematic approach maintains data accuracy in web scraping at scale.
Verify Data Freshness and Timestamps
Data quality deteriorates over time as real-world information changes. We must validate scraped data freshness to ensure our information remains current and actionable. Stale data leads to poor decisions even when technically accurate at the time of collection.
We capture extraction timestamps for every single record in our database. This metadata enables age-based filtering and identifies data requiring refresh. Each timestamp includes date, time, and timezone information for precise tracking.
Our freshness verification system monitors several indicators:
- Compare extracted data against known update patterns for each source
- Flag records that haven't changed across multiple scraping sessions
- Implement change detection comparing new scrapes against previous versions
- Establish refresh schedules appropriate to each data type's volatility
- Alert when staleness exceeds acceptable thresholds for critical data
Product prices that remain identical for six months may indicate stale data. We cross-reference these suspicious patterns with source website update frequencies. Most e-commerce sites update pricing at least monthly.
Change detection systems compare current scrapes against historical versions. When we detect zero changes across multiple extraction sessions, we investigate whether our scraper functions correctly. Complete stability often signals technical problems.
Different data types require different refresh intervals. Stock prices need minute-by-minute updates, while company addresses might stay current for months. We tailor our verification approach to match each data element's expected change frequency.
Statistical Anomaly Detection
Statistical methods identify suspicious patterns that suggest data quality problems. We analyze distributions, outliers, and patterns to spot errors that individual record validation might miss. This approach answers how to verify scraped web data at scale using mathematical rigor.
We calculate distributions for all numeric fields in our datasets. Values falling beyond three standard deviations from the mean trigger anomaly alerts. A product priced at $2,500 when 98% of similar products cost between $20-$100 requires verification.
Benford's Law provides a powerful tool for detecting fabricated numeric data. In naturally occurring datasets, leading digits follow predictable patterns, about 30% of numbers start with "1," while only 4.6% start with "9." Significant deviations suggest data manipulation or systematic errors.
Suspiciously repetitive values indicate extraction errors. When we see the same price appearing for 85% of products, we investigate whether our scraper extracted a default value. Real-world data shows natural variation.
We monitor extraction rates across scraping sessions to detect sudden drops in data completeness. If our scraper typically captures 95% of targeted fields but suddenly drops to 60%, this signals technical problems. Website structure changes often cause these patterns.
Our Python implementation tracks these statistical measures automatically:
- Calculate mean, median, and standard deviation for numeric fields
- Apply Benford's Law tests to financial and quantity data
- Monitor field completion rates across scraping sessions
- Identify suspiciously uniform distributions that suggest errors
- Generate alerts when statistical patterns deviate from baselines
Tuning sensitivity balances catching errors against false positive alerts. We adjust thresholds based on each dataset's characteristics and acceptable risk levels. High-stakes applications use stricter detection parameters than exploratory projects.
These advanced techniques work together to verify scraped data with exceptional accuracy. Cross-referencing confirms correctness, logical validation catches impossible values, freshness checks ensure currency, and statistical analysis spots systematic problems. Combined, they provide complete quality assurance for your web scraping projects.
Automated Data Verification for Scraping at Scale
Scraping at scale requires automated verification systems that process data without human intervention. Handling thousands or millions of records daily makes manual checks a bottleneck. We need systems that verify data quality automatically, maintaining high throughput and accuracy.
Building verification processes that run continuously is key to successful scraping at scale. These systems catch errors immediately, not weeks later. They also reduce costs significantly, batch HTML preprocessing can reduce token usage by 60-80% with AI-powered extraction tools.
Designing Verification Pipelines That Scale
We architect our automated data verification pipelines using modular components that work independently. Each verification stage is a discrete unit you can develop, test, and scale separately. This gives you flexibility as your scraping needs grow.
Queue-based processing forms the backbone of effective scraped data verification at scale. Scraped records flow through verification queues where each stage performs specific checks. Dead-letter queues capture failed validations automatically for later review.
Here's how we structure our verification pipelines:
- Input validation stage: Checks data format and completeness before deeper processing
- Schema verification stage: Ensures all required fields exist with correct data types
- Business logic validation: Applies domain-specific rules to catch logical inconsistencies
- External verification stage: Calls third-party APIs for email, phone, or address validation
- Output formatting stage: Standardizes verified data for downstream systems
We use orchestration tools like Apache Airflow or Prefect to manage dependencies between verification steps. These platforms handle complex workflows automatically and provide visibility into every stage.
Building retry logic with exponential backoff ensures temporary failures don't derail your entire pipeline. When a verification step fails, the system waits progressively longer before retrying. This prevents overwhelming external APIs during outages.
We implement fast-path validation for obviously clean data. Records that pass initial quick checks skip intensive verification steps. This approach balances thoroughness with processing speed, suspicious records get extra scrutiny while clean data moves through quickly.
Accelerating Verification with Parallel Processing
Processing records sequentially becomes impossibly slow when scraping at scale. Parallel processing distributes verification tasks across multiple CPU cores or machines simultaneously. This dramatically improves throughput without sacrificing accuracy.
Python's multiprocessing module lets us distribute CPU-intensive verification across available cores. For I/O-bound tasks like API calls, we use asyncio for asynchronous processing. The choice depends on where your verification bottleneck occurs.
Implementing semaphores helps control concurrent requests to external verification APIs. This prevents triggering rate limits or anti-bot detection. We set appropriate concurrency levels based on API documentation and available resources.
Here are our parallel processing strategies for scraped data verification at scale:
- Batch processing: Group similar verification tasks together for efficient API usage
- Worker pools: Maintain multiple verification workers that pull from shared queues
- Rate limiting: Add polite pacing between requests to respect server resources
- Result aggregation: Collect verification results safely across parallel processes
We've found that parallel processing overhead exceeds benefits for datasets under 1,000 records. The setup time and coordination costs outweigh speed gains. For larger datasets, parallelization can improve throughput by 5-10x depending on verification complexity.
Proper error handling in parallel verification prevents one failed task from crashing the entire system. We implement try-catch blocks around each verification unit and log failures for investigation. Resource cleanup ensures processes don't leave connections or file handles open.
Monitoring Quality Continuously
Verification isn't a one-time event, it's an ongoing process that requires constant monitoring. We track data quality metrics over time to spot degradation before it impacts business operations. Real-time dashboards provide visibility into verification health.
Our continuous quality monitoring systems display key metrics like pass rates, failure reasons, and processing throughput. When validation pass rates suddenly drop, it often indicates source website changes that broke our scrapers. Early detection prevents bad data from reaching production systems.
We set up alerts for quality degradation patterns:
- Sudden drops: Pass rates falling more than 20% trigger immediate alerts
- Gradual trends: Slowly declining quality over weeks indicates structural issues
- Anomaly detection: Statistical outliers in verification metrics warrant investigation
- Throughput issues: Processing slowdowns suggest infrastructure problems
Integration with monitoring platforms like Grafana gives us customizable dashboards and powerful query capabilities. We maintain historical quality data for compliance documentation and improvement analysis. This data helps us understand which verification steps provide the most value.
Tracking quality trends reveals patterns you'd miss checking individual records. For example, we might notice validation failures spike during specific times of day when target websites update content. This insight helps us adjust scraping schedules for better data quality.
Advanced Verification Techniques for Complex Projects
Dealing with the most challenging web scraping projects pushes us to explore advanced verification methods. These include browser automation, machine learning detection, and custom validation logic. When we face sophisticated websites with dynamic content, anti-bot protections, and user-generated content, our standard verification methods need a significant upgrade. Such complex scenarios demand specialized tools and techniques that go beyond basic schema validation.
We've developed a toolkit to tackle these advanced verification challenges. Our approach combines multiple technologies to ensure data accuracy in the most difficult scraping environments.
Validating Dynamic Content and JavaScript-Heavy Sites
Modern websites increasingly rely on JavaScript to render content after the initial page load. This creates significant verification challenges because the data we need might not exist in the original HTML response. We need to ensure that JavaScript has fully executed before we attempt to extract and verify any data.
Our verification strategy for dynamic content focuses on wait mechanisms that confirm complete rendering. We implement several approaches depending on the site architecture.
For sites with predictable loading patterns, we wait for specific DOM elements to appear. This ensures the javascript has created the content we need to scrape. For more complex applications, we monitor network activity until all API calls complete and the page reaches an idle state.
Single-page applications present unique verification challenges. Navigation doesn't trigger traditional page loads, so we must verify state changes through URL monitoring and DOM mutations. We've found that checking for routing changes and waiting for view-specific elements provides reliable verification signals.
- Element visibility checks: Confirm target elements are present and visible in the rendered DOM
- Network idle monitoring: Wait until all AJAX requests and API calls complete before extraction
- Custom JavaScript execution: Run verification scripts directly in the browser context to check application state
- Screenshot comparison: Capture visual snapshots to verify complete rendering against expected layouts
We also validate completeness by checking for pagination indicators and infinite scroll triggers. If these elements suggest additional content should load, our verification flags the data as incomplete until we capture everything.
Implementing Browser Automation Frameworks Effectively
Both playwright and selenium serve as powerful frameworks for browser automation, but they require careful configuration for effective verification. We've migrated most of our projects to Playwright due to its superior performance and modern async architecture, though Selenium remains valuable for specific legacy requirements.
Stealth configuration is critical for both frameworks. Modern anti-bot systems detect automation by checking for WebDriver properties, missing browser features, and unnatural interaction patterns. We remove these telltale signs by disabling automation flags and adding realistic browser fingerprints.
Our playwright implementation uses context options that mask automation indicators:
- User-agent randomization: Rotate realistic browser signatures from actual devices
- Viewport variation: Use different screen resolutions to simulate diverse users
- Timezone and locale settings: Match geographic targeting to avoid inconsistencies
- WebGL and canvas fingerprints: Add realistic graphics rendering characteristics
Complex interactions require scripted behaviors that mimic human users. We implement gradual scrolling with random delays to trigger lazy-loading content. Multi-step forms receive realistic typing speeds with occasional corrections. Authentication flows include natural pauses between field entries.
The selenium WebDriver API differs from Playwright's approach, using synchronous calls instead of async/await patterns. For teams with existing Selenium infrastructure, we recommend gradually transitioning to Playwright for new projects while maintaining Selenium for stable production scrapers.
Building Custom Validators in Python
Generic verification tools can't address every project's unique requirements. We build custom verification scripts in python that implement domain-specific business rules and complex multi-field validations.
Our approach creates reusable validation functions organized into libraries. Each validator encapsulates specific verification logic that we can apply across different scraping projects. This modularity improves code maintainability and testing coverage.
A product data validator might check pricing against historical ranges:
- Price reasonability checks: Flag prices that fall outside expected ranges for product categories
- Currency consistency validation: Ensure monetary values match declared currency codes
- Discount logic verification: Confirm that sale prices are actually lower than regular prices
- Historical trend comparison: Compare current prices against time-series data to identify anomalies
Contact information validators integrate external APIs to confirm accuracy. We verify business addresses against geocoding services, check phone numbers through carrier lookup databases, and validate email domains against DNS records.
Content validators examine article metadata for internal consistency. Publication dates should precede update timestamps. Author names should match contributor databases. Category assignments should align with content analysis results.
These custom python validators become organizational assets that codify data quality standards. New team members can apply established verification rules without understanding every business constraint. Quality benchmarks remain consistent across projects and over time.
Best Practices for Maintaining Verified Scraped Data Quality
Ensuring long-term data quality requires a commitment to ongoing verification. Initial validation offers temporary confidence, but the real challenge lies in maintaining that quality over time. This involves treating verification as a continuous process, not just a one-time task.
To maintain web data quality, we employ systematic approaches. These include addressing information decay, documenting processes, continuous monitoring, and improvement cycles. Such practices transform verification into a sustainable capability within an organization.
Establish Regular Re-Verification Schedules
Data verification is not a one-time task. Information degrades constantly due to changing circumstances. Email addresses become invalid when employees leave, businesses close or relocate, and product catalogs update daily.
We schedule re-verification based on data type volatility. Stock prices need daily validation, contact information monthly checks, and business attributes quarterly cycles.
When resources are limited, prioritization is key. We focus on the most critical datasets, those driving revenue decisions or regulatory compliance. Our system flags high-value records for more frequent validation.
Automation enables sustainable re-verification at scale. We configure workflows for automated checks without manual initiation. This ensures data remains current without constant human intervention.
Decision frameworks determine optimal verification frequency. We consider the data's business value and expected change rate. High-value, rapidly changing data is verified most frequently.
Incremental verification techniques optimize resources further. We focus on records most likely to have changed, reducing verification costs by 60-70% while maintaining data accuracy.
Document Your Data Scraping Verification Process
Comprehensive documentation ensures consistency, enables team scaling, and supports compliance. Without clear documentation, verification processes rely on individual knowledge that disappears when team members leave.
We create verification runbooks detailing every validation rule and its rationale. These runbooks answer critical questions, ensuring consistency in verification processes.
Data dictionaries define each field in our datasets. They specify valid values, formats, and verification requirements. This standardization prevents interpretation inconsistencies.
API configurations and credentials for verification services must be documented systematically. We maintain secure records of verification services, their configurations, and authentication details.
Quality thresholds and acceptance criteria vary by data type. Our documentation specifies minimum pass rates for each verification category. For example, we require 95% validation success for email addresses but accept 85% for phone numbers in certain contexts.
Change logs track modifications to the verification process over time. When we adjust validation rules or add new checks, we document the change, the reason, and the expected impact. This historical record proves invaluable for troubleshooting quality degradation.
Documentation templates standardize information capture. We provide teams with pre-formatted documents for consistent coverage of essential verification details across different scraping projects.
Monitor Data Accuracy in Web Scraping Over Time
Tracking quality trends reveals gradual degradation before it impacts business decisions. We establish baseline quality metrics when first implementing verification processes. These baselines provide reference points for measuring improvement or decline.
Rolling averages of verification pass rates highlight trends that single measurements might miss. A 30-day moving average smooths daily fluctuations and reveals whether web data quality is improving, stable, or degrading.
Comparing quality across different data sources identifies problematic targets. If one website consistently produces lower verification pass rates, we investigate whether the issue stems from poor source data, inadequate extraction logic, or overly strict validation rules.
Segmenting quality analysis by data field pinpoints specific validation failures. We might discover that street addresses verify successfully 98% of the time while postal codes fail 15% of validations, indicating a targeted problem requiring specific attention.
Quality dashboards visualize trends and make degradation immediately visible to stakeholders. We build dashboards that display:
- Current verification pass rates by data type
- Trend lines showing quality trajectory over the past 90 days
- Comparison charts highlighting differences across data sources
- Alert indicators when quality falls below defined thresholds
SQL queries and Python scripts calculate common quality metrics from verification logs. We automate metric calculation so teams can focus on interpretation. These automated reports run daily and distribute to relevant stakeholders.
Create Feedback Loops for Continuous Improvement
Verification results provide valuable intelligence for improving both scraping and validation processes. We analyze verification failures systematically to identify patterns. For example, discovering that 60% of email verification failures originate from one website section suggests extraction logic problems.
Failed validations guide refinement of extraction selectors. When specific fields consistently fail verification, we revisit the CSS selectors or XPath expressions used to extract that data. This iterative improvement increases accuracy at the source.
We incorporate verification feedback into scraper development cycles. Each iteration aims to improve accuracy based on validation results from previous runs. This approach systematically eliminates extraction errors over time.
Regular review meetings bring stakeholders together to examine quality metrics and prioritize improvements. We schedule monthly sessions where data engineers, business analysts, and verification specialists discuss trends and plan enhancements.
Categorizing verification failures reveals appropriate responses. We classify failures into three categories:
- Scraping logic errors: Problems with extraction selectors, parsing logic, or data transformation that should be fixed in the scraper code
- Poor source data quality: Inherently problematic information on target websites that may require alternative sources or acceptance of lower quality
- Overly strict validation rules: Verification criteria that reject legitimate data and should be relaxed to match real-world variability
Each category demands different corrective action. Scraping errors get fixed immediately. Source quality issues trigger evaluation of alternative data sources. Strict rules are carefully relaxed after validating that changes won't admit truly invalid data.
Quality review meeting templates ensure consistent coverage of essential topics. Our template includes sections for reviewing quality trends, discussing major failures, evaluating improvement initiatives, and prioritizing next steps. This structure keeps meetings focused and productive.
Improvement tracking systems document initiatives and measure their impact. When we implement changes to verify scraped data more effectively, we track baseline metrics, the intervention date, and post-change measurements. This approach validates that improvements deliver expected benefits.
Continuous improvement transforms verification from a static checkpoint into a dynamic capability that evolves with your scraping needs. By establishing these best practices, we ensure that verified scraped data maintains its quality and reliability throughout its entire lifecycle.
Conclusion
Web data quality is key to success in web scraping projects. We've explored seven essential steps to ensure the accuracy of scraped data. These steps range from strategy design to real-time validation, using specialized tools and cross-validation techniques. Each step fortifies your data against inaccuracies.
In 2026, verification tools are more accessible than ever. ApexVerify simplifies contact validation at scale. Python libraries handle complex checks automatically. AI adapts to website changes, making data accuracy affordable for all, not just large enterprises.
Begin verifying your scraped data today. Start with basic checks and gradually add more advanced techniques. Monitor your progress and refine your methods based on real results. This will help you improve your data's accuracy.
Investing in data verification pays off in many ways. Marketing campaigns improve, business intelligence becomes more reliable, and automation systems run more smoothly. Your strategic decisions will be based on solid data.
Remember, verification is an ongoing process. As websites and data sources evolve, so must your verification methods. The foundation you establish today will support your data-driven success for years.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between data validation and data verification in web scraping?
Validation and verification are two distinct processes in ensuring data quality. Validation checks if the data fits expected schemas and formats. It ensures data is technically correct, like an email address being properly formatted. Verification, on the other hand, confirms the data's factual accuracy and real-world truth. It checks if an email address actually exists and can receive messages.
We use both validation and verification in our workflows. Validation catches technical errors during extraction. Verification ensures the data is genuinely correct and usable. Both are essential for maintaining high-quality scraped datasets.
How does ApexVerify help with verifying scraped contact data at scale?
What are the most common data quality issues that affect scraped datasets?
Should I use Python with BeautifulSoup, Selenium, or Playwright for web scraping?
How do I bypass Cloudflare, Akamai, and other bot detection systems when scraping?
What is the best way to handle Captcha and Google reCAPTCHA during scraping?
How do I verify email addresses scraped from websites to avoid high bounce rates?
What are the key differences between HTTP proxies, SOCKS5 proxies, and SOCKS4 proxies for web scraping?
How do I verify phone numbers scraped from websites to ensure they're valid and active?
What is the difference between a headless browser and an antidetect browser for web scraping?
How can I verify physical addresses scraped from websites to ensure they're deliverable?
What are the best practices for managing User-Agent strings and HTTP headers in web scraping?
What is the best way to deduplicate scraped data while maintaining data integrity?
What are elite proxies and when should I use them for web scraping?
How often should I re-verify scraped data to maintain quality over time?